Contact Stockwell Elastomerics
Request a quote or get more information.
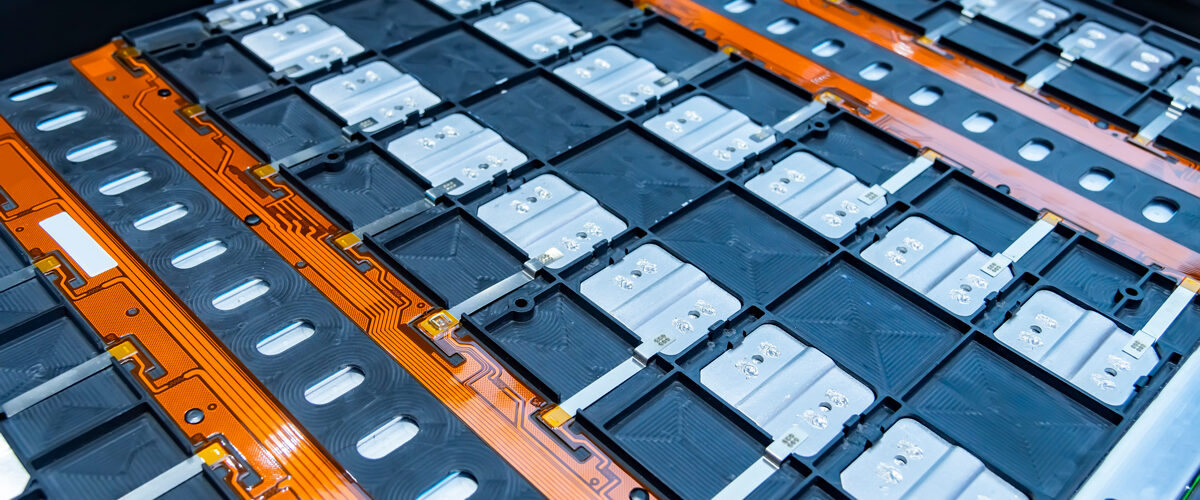

This article serves as a primer for industry professionals who are seeking information that can support their own product designs. Solid state batteries are used in electric vehicles (EVs), but there are also specialized applications such as grid scale energy storage, portable medical equipment, satellites, and uncrewed systems. The solid electrolytes that are used are more expensive to produce, but they offer advantages over liquid and gel electrolytes.
Battery electrolytes are substances that allow electrically charged particles (ions) to flow between two terminals (electrodes). By enabling this flow, electrolytes facilitate the electrochemical reactions that power batteries. The ideal electrolyte provides high energy density, high ionic conductivity, chemical stability, nonflammability, and high mechanical strength. Electrical insulation and stability within a battery’s operating voltage and temperature range are also required.
Traditionally, liquid or gel electrolytes have been used in the rechargeable lithium ion batteries found in many EVs and laptop computers. Liquid electrolytes facilitate rapid charging and discharging, and gel electrolytes mitigate the risk of leakage. To produce liquid electrolytes, a salt is dissolved in a liquid solvent. To produce gel electrolytes, a liquid electrolyte is combined with a gelling agent. Liquids and gels have advantages, but they do not meet all the requirements for an ideal electrolyte.
Today, solid state batteries are becoming more popular, especially for EVs. They support greater ranges, faster charging, better cold weather performance, and improved fire safety. The solids that are used can be inorganic or polymer based. Ceramic electrolytes are especially promising because they meet many of the performance requirements for an ideal electrolyte; however, they require expensive high temperature treatments.
Several companies are preparing to produce or scale up production of solid state batteries. There are university based advances as well. For example, Japan’s Kyoto University is developing fluoride ion batteries and exploring various materials for the cathode. As reported by Cornell University, researchers have performed experiments with ultra high frequency self heating (UHFSH) on symmetric solid state cells using lithium aluminum germanium phosphate (LAGP) electrolytes.
Stockwell Elastomerics will continue to monitor advances in solid state battery technology and invites industry professionals to contact the Applications Engineering Team for high performance materials and products such as custom silicone gaskets.
Request a quote or get more information.